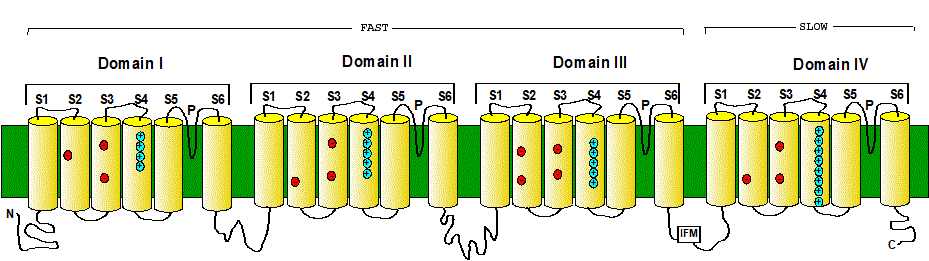

SODIUM CHANNEL ALPHA SUBUNIT
The alpha subunit is the pore forming subunit of the sodium channel. This alpha subunit is a single polipeptide with four homologous domains. Each domain has 6 transmembrane segments (S1 through S6) plus a pore loop. Each domain has a voltage sensor composed of segments S1 through S4, where S4 segment has the gating charges, similar to the K channel. Sensors of Domain I, II and III have fast kinetics while domain IV sensor is about 8 times slower. The four sensors control the activation gate that opens and close the conducting pore. Even when activated (open gate) conduction is prevented by inactivation which is mediated by the inactivating particle that contains the IFM motif.
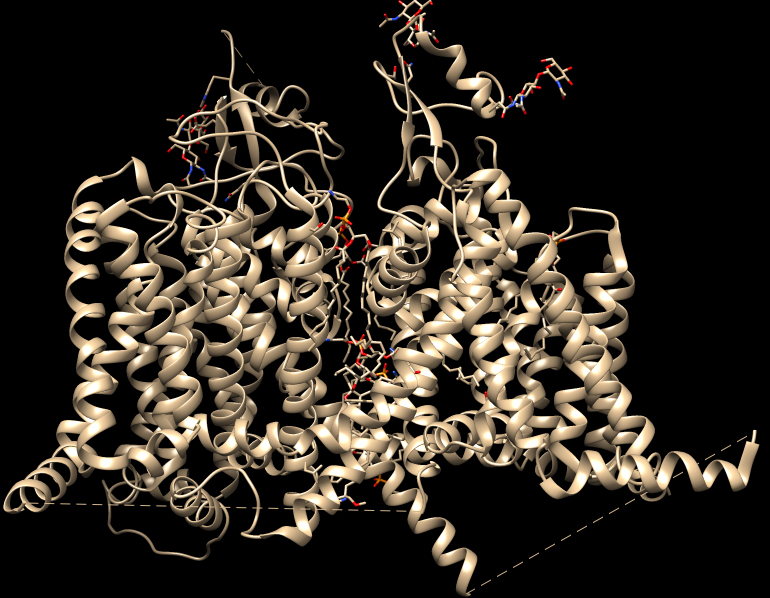
 The picture on the left is the
structure of the alpha subunit of the human skeletal muscle Na channel (Nav1.4,
6aff.pdb) showing the four Domains forming a central conduction pore. The
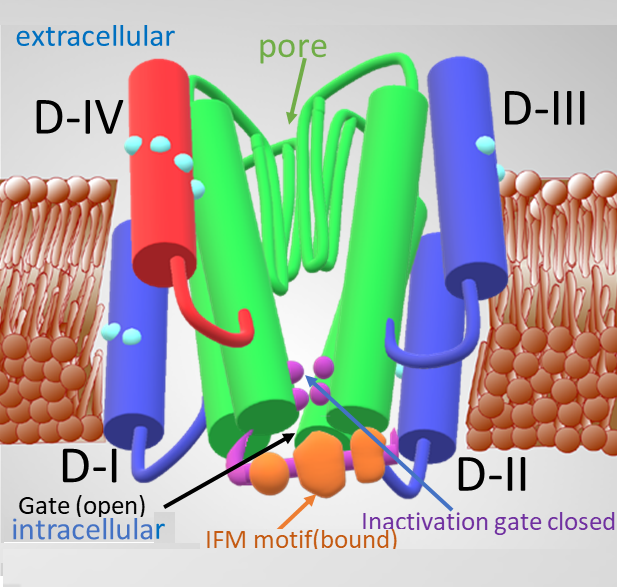
picture on the right is an schematic view of the alpha subunit
of the Na channel where the voltage sensors (comprised of segments S1 through
S4) have been simplified to only the S4 segment. The pore region (S5, S6 and
pore loop) have been simplified to the S6 segments and part of the pore loop.
This schematic view is used in the simulation of Na
channel operation under voltage clamp
The picture on the left is the
structure of the alpha subunit of the human skeletal muscle Na channel (Nav1.4,
6aff.pdb) showing the four Domains forming a central conduction pore. The
picture on the right is an schematic view of the alpha subunit
of the Na channel where the voltage sensors (comprised of segments S1 through
S4) have been simplified to only the S4 segment. The pore region (S5, S6 and
pore loop) have been simplified to the S6 segments and part of the pore loop.
This schematic view is used in the simulation of Na
channel operation under voltage clamp