Membrane voltage as a function of space and time in a passive axon.
This is an axon with all the voltage dependent conductances blocked. The stimulus is a current step I injected at x=0, starting at time t=0.
The time constant (tau) represents the time it takes to charge the membrane patch to (1-1/e)=0.63 of its final value.It is given by:
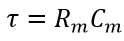
Where Rm is the membrane resistance (in Kohm cm^2) and Cm is the membrane capacitance in uF/cm^2.
The space constant (lambda) represents the distance at which the voltage decays to 1/e=0.37 of it maximum value in the steady state.It is given by
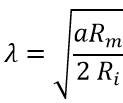
Where a is the radius of the axon (in cm) and Ri is the internal resistivity of the axoplasm (in Kohm cm). start initiates the I step.
The Voltage can be plotted as a function of distance as times evolves (V vs X) or as a function of time at five different places (V vs T),
This is an axon with all the voltage dependent conductances blocked. The stimulus is a current step I injected at x=0, starting at time t=0.
The time constant (tau) represents the time it takes to charge the membrane patch to (1-1/e)=0.63 of its final value.It is given by:
Where Rm is the membrane resistance (in Kohm cm^2) and Cm is the membrane capacitance in uF/cm^2.
The space constant (lambda) represents the distance at which the voltage decays to 1/e=0.37 of it maximum value in the steady state.It is given by
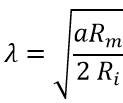
Where a is the radius of the axon (in cm) and Ri is the internal resistivity of the axoplasm (in Kohm cm). start initiates the I step.
The Voltage can be plotted as a function of distance as times evolves (V vs X) or as a function of time at five different places (V vs T),